By: Matthew Price

Watercolor pencil
The short-beaked common dolphins are known by their scientific name as Delphinus delphis. Their taxonomic classifications are the kingdom Animalia, phylum Chordata, class Mammalia, order Cetacea, family Delphinidae, genus Delphinus, and species Delphis.
This particular breed of common dolphins are found in multiple regions of the world. They are spread out across many oceans and can be found off the U.S. west coast, east coast, South African coast, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Southern Pacific. (Westgate,88) Fin and flipper locomotion is the main mode of swimming locomotion in the common dolphins.

A short-beaked common dolphin jumps out of the water. Pencil, watercolor pencil drawing
The physical characteristics in the average adult common dolphin ranges between 6.2-8.2 ft long and can weigh up to 176-518 lbs. The population of the species is extremely abundant in numbers and widely spread out across the globe. Their skin color is grey. The food chain of the common dolphins largely consists of fish and cephalopods. Fish make up 90% of their diet by numbers (N) and 53% by mass (M) whereas cephalopods account for 9%N and 46%M. (Pusineri, Maginin, Meynier, Spitz, Hassani, Ridoux)
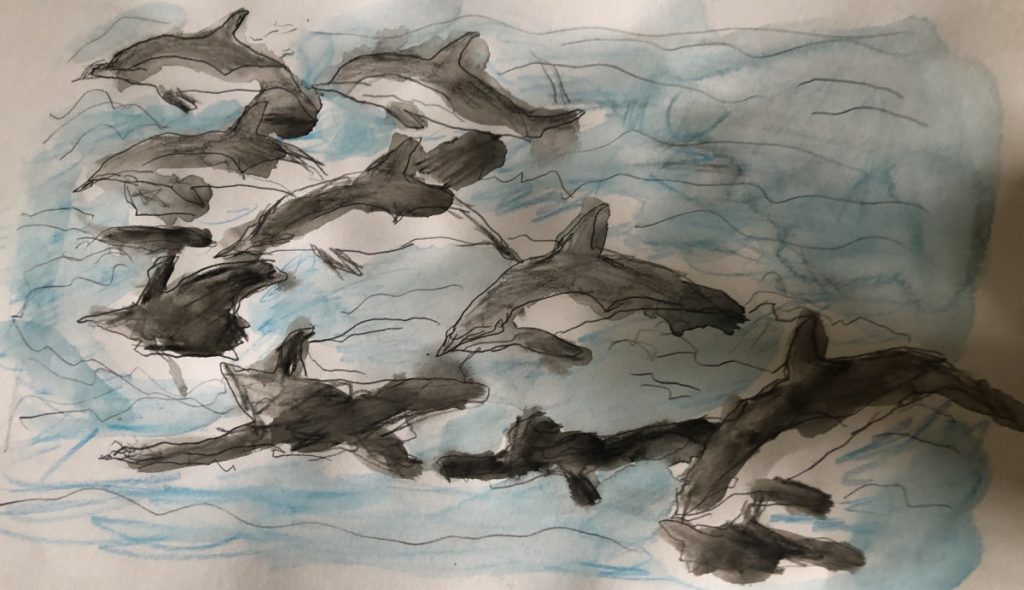
The common dolphins often travel in groups. Their feeding behaviors show that they often form a feeding swarm. These feeding swarms range from 30 to 120 dolphins and are classified by the size of the group (Gallo Reynoso, 254-55). As dolphins search for large schools of fish, they travel at high speeds and jump out of the water at high heights. When the school is spotted, the swarm of dolphins slow down and form a U shape. The formation is utilized to call for larger groups to close in and surround the fish through ultrasonic sounds emitted for echolocation (Gallo Reynoso, 256-57).

When it comes to mating, the male common dolphins interacts competitively with other males and searches for receptive females. When they find a mate, the males spend very little time with their mates because they seek a partner for the sole purpose of mating. Sometimes, the male defends the female by themselves or with a large group of males. The female common dolphins often mate with more than one male. (Murphy, Collet, Rogan, 86)
Short-beaked Common Dolphin Animation
Umwelt
The short-beaked common dolphins love to play in nearly every ocean on the planet. They love to jump out of the water and perform backflips both in and out of the water. They often put on their shows under the surface in front of large groups of fish in the hopes of lurring their prey. However, for the people living on the surface, they only do their tricks from far distances. They know all too well what would happen if they got too close to land.
All Images copyrighted by Matthew Price
Bibliography
Pusineri, C., Magnin, V., Meynier, L., Spitz, J., Hassani, S., & Ridoux, V. (2007). Food And Feeding Ecology Of The Common Dolphin (Delphinus Delphis) In The Oceanic Northeast Atlantic And Comparison With Its Diet In Neritic Areas. Marine Mammal Science, 23(1), 30–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-7692.2006.00088.x
Westgate, A. J. (2007). Geographic Variation in Cranial Morphology of Short-beaked Common Dolphins (Delphinus delphis) from the North Atlantic. Journal of Mammalogy, 88(3), 678–688. doi: 10.1644/06-mamm-a-177r.1
Murphy, S., Collet, A., & Rogan, E. (2005). Mating Strategy In The Male Common Dolphin (Delphinus Delphis): What Gonadal Analysis Tells Us. Journal of Mammalogy, 86(6), 1247–1258. doi: 10.1644/1545-1542(2005)86[1247:msitmc]2.0.co;2
van der Land, J., & Perrin, W. (2004, December 21). www.marinespecies.org. Retrieved August 20, 2008, from http://marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=137094
Gallo Reynoso, J. P. (1991). (PDF) Group behavior of common dolphins (Delphinus delphis … Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/236632979_Group_behavior_of_common_dolphins_Delphinus_delphis_during_prey_capture
Short-Beaked Common Dolphin. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/species/short-beaked-common-dolphin#overview
